Imaging Biomarkers: Complete Guide to Medical Diagnostic Indicators | 2024 Update
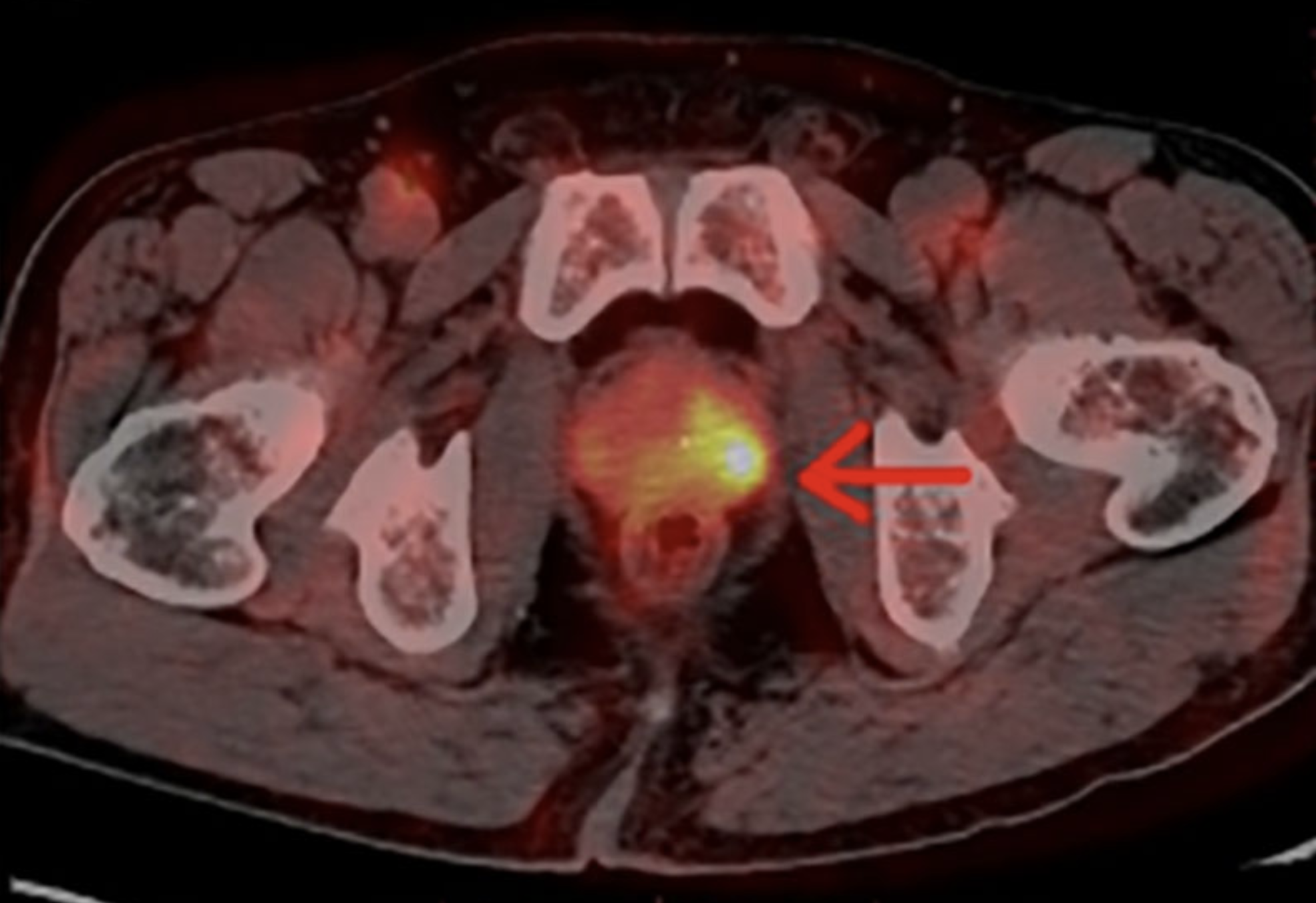
Imaging biomarkers represent a revolutionary advancement in modern medicine, offering quantifiable measurements that transform how we detect, diagnose, and monitor diseases. These sophisticated tools have become increasingly crucial in both clinical practice and research settings, providing healthcare professionals with objective data to make more informed decisions about patient care.
What Are Imaging Biomarkers?
The concept of imaging biomarkers has evolved significantly over recent years, becoming increasingly precise in its definition and application. According to the FDA/NIH Biomarker Working Group, a biomarker is:
"a defined characteristic that is measured as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or responses to an exposure or intervention, including therapeutic interventions"
This definition encompasses both quantitative and qualitative measurements derived from medical images.
Also Read: DICOM Modalities: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Imaging Technologies
Applications in Clinical Practice
The clinical applications of imaging biomarkers span across multiple medical disciplines and scenarios. These powerful tools have revolutionized how healthcare providers approach diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring. The integration of imaging biomarkers into clinical workflows has created new possibilities for personalized medicine and improved patient outcomes.
Disease Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection and accurate diagnosis remain critical challenges in modern medicine. The National Cancer Institute states:
"Biomarker testing is a way to look for genes, proteins, and other substances (called biomarkers or tumor markers) that can provide information about cancer. Each person's cancer has a unique pattern of biomarkers."
Also Read: Cancer Imaging: Complete Guide to Diagnostic Tests & Technologies
Treatment Monitoring and Response Assessment
The implementation of imaging biomarkers in treatment monitoring has transformed how clinicians evaluate therapeutic effectiveness. According to research published in Biomarker Research:
"They can be used to screen healthy patients for malignancy, estimate the prognosis, predict the outcome from therapy, and monitor disease."
Validation and Standardization
The journey from discovering an imaging biomarker to implementing it in clinical practice requires rigorous validation and standardization processes. These steps ensure that measurements are reliable, reproducible, and clinically meaningful across different healthcare settings and patient populations.
Also Read: The Ultimate Guide to Preprocessing Medical Images
Types of Imaging Biomarkers
The field of imaging biomarkers encompasses various types of measurements and indicators, each serving specific purposes in medical diagnosis and monitoring. Understanding these different categories helps healthcare providers select the most appropriate biomarkers for their specific clinical needs. The advancement of imaging technology has enabled increasingly sophisticated measurements across multiple modalities.
Anatomical Biomarkers
Anatomical imaging biomarkers provide crucial structural information about tissues and organs. These measurements include:
- Tumor size and volume
- Organ dimensions
- Tissue density
- Structural alterations
Functional and Molecular Biomarkers
Functional and molecular imaging biomarkers offer insights into biological processes at the cellular level. These include measurements of:
- Metabolic activity
- Blood flow
- Receptor expression
- Cellular function
Also Read: DICOM Modalities: A Comprehensive Guide to Medical Imaging Technologies
Quality Assurance and Implementation
The successful implementation of imaging biomarkers requires robust quality assurance protocols and standardized procedures. Healthcare facilities must establish comprehensive frameworks to ensure reliable and reproducible results. This systematic approach encompasses equipment calibration, staff training, and ongoing monitoring of measurement accuracy.
Standardization Protocols
Three essential components drive successful standardization:
- Equipment Calibration and Maintenance
- Staff Training and Certification
- Data Collection and Analysis Protocols
Also Read: Medical Imaging Research: 2024 Breakthroughs in AI and Advanced Technologies
Future Directions and Emerging Technologies
The landscape of imaging biomarkers continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological advances and increasing understanding of disease processes. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming how we analyze and interpret imaging biomarkers, leading to more accurate and efficient diagnostic processes.
Artificial Intelligence Integration
AI and machine learning are transforming how we analyze and interpret imaging biomarkers. Artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques are helping researchers and clinicians to extract more detailed and precise information from medical images than ever before.
Emerging Applications
New applications for imaging biomarkers continue to emerge across various medical fields:
- Neurodegenerative Disease Monitoring
- Cardiovascular Risk Assessment
- Therapeutic Response Prediction
- Early Cancer Detection
Also Read: Collective Minds Research for CROs
Summary
Imaging biomarkers have transformed modern medicine by providing quantifiable measurements for disease detection, monitoring, and treatment assessment. Their continued evolution, supported by technological advances and standardization efforts, promises even greater impact on healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
FAQ
What makes an imaging biomarker clinically valuable?
A clinically valuable imaging biomarker must demonstrate reproducibility, accuracy, and clear correlation with clinical outcomes. It should provide meaningful information that directly influences patient care decisions.
How do imaging biomarkers complement traditional diagnostic methods?
Imaging biomarkers provide non-invasive, quantitative measurements that complement conventional diagnostic approaches. They often detect disease-related changes before they become apparent through traditional methods.
What role do imaging biomarkers play in personalized medicine?
Imaging biomarkers enable personalized treatment approaches by providing detailed information about individual disease characteristics and treatment responses, allowing for more targeted therapeutic strategies.

Reviewed by: Mathias Engström on November 6, 2024




